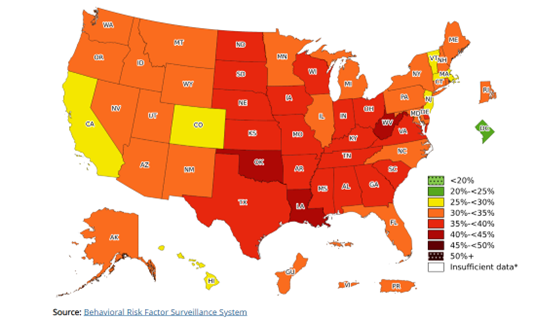
Highway to Health: Obesity
Obesity is defined as abnormal or excessive fat that presents a risk to a person’s health. Being obese can raise the risk of many other problems, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, asthma and more.
In the past, obesity was thought to be an issue of self-control; now we know that it is a complex disease caused by a variety of factors. These factors include eating habits, physical activity, sleep routines, genetics, medications, and social determinants of health.
The goal of obesity treatment is to reach and maintain a healthy weight and to reduce the risk of secondary complications. A loss of as little as five to 10 percent of body weight can significantly reduce the risk of other health complications.
There is no secret recipe or single best diet for weight loss. All approaches to weight loss recommend improving eating habits and increasing physical activity. This may involve reducing calorie intake, increasing dietary fiber, eating more fruits and vegetables, and utilizing meal replacement options. Additional treatment may include the addition of medications or surgical procedures, but these should only be undertaken in consultation with your doctor.